Introduction
Direct-to-film printing has changed how designs move onto fabrics and other materials, especially with heavy reliance on white ink layers. Operations often face inconsistencies that affect output reliability and final appearance. White ink settles unevenly, colors lack depth on dark substrates, or static causes powder to clump in wrong places. These issues frequently stem from limitations in the base coating on PET film.
Advanced white ink absorbent coatings directly address these challenges. How white ink absorbent coating improves print quality becomes clear when examining stability during long runs, color density in transfers, and control over static interference. Integrated formulations handle multiple functions in one layer, delivering steadier results than older multi-step approaches.
A custom apparel shop running high-volume orders once dealt with frequent nozzle checks and color adjustments mid-job. Switching to a unified coating reduced those interruptions noticeably, allowing smoother production and brighter outcomes on varied textiles. Similar patterns emerge across label and packaging work, where precision matters most.
Key Factors Affecting DTF Print Quality
Several elements influence consistency in DTF processes on PET film.
Print stability stands out as a primary concern. White ink, thicker than standard colors, tends to settle or flow unpredictably without proper surface reception. This leads to banding or gaps during extended printing sessions.
Color density follows closely. Weak white bases allow subsequent layers to appear muted, particularly on black or deep-toned fabrics. Achieving vibrant saturation requires a solid, opaque underlayer that holds pigments effectively.
Anti-static properties play a subtler yet critical role. Static buildup attracts adhesive powder unevenly or repels ink droplets, creating clusters or voids. Dry environments worsen this, turning minor charges into visible defects.
These factors compound in real settings. A promotional merchandise run for events might start strong but degrade over hundreds of sheets as static accumulates or ink properties shift. Understanding interactions between ink, coating, and environment guides better material choices.
Enhancing Print Stability with Absorbent Coatings
Stability in printing demands consistent ink behavior from first sheet to last.
Strong absorbent coatings draw white ink rapidly into a microporous structure, preventing surface migration that causes streaking. This quick uptake keeps lines sharp and fills solid even in dense areas.
Integrated single-layer designs contribute here. Unlike traditional systems requiring separate release and absorption steps, unified coatings maintain uniformity across the roll. Delamination risks drop, reducing interruptions from coating separation under heat or tension.
Temperature resistance adds another layer of reliability. Formulations that withstand curing conditions without softening ensure ink remains locked during powder application and pressing.
In practice, a textile decorator handling daily runs of several thousand transfers found far fewer pauses for cleaning or recalibration after adopting such coatings. Output stayed predictable even during peak seasons.
Achieving Greater Color Density

Vibrant, opaque transfers depend heavily on the white ink foundation.
Effective coatings create a dense, even white base that blocks substrate show-through. Porous matrices hold higher ink volumes without overflow, building opacity that supports bright overlays.
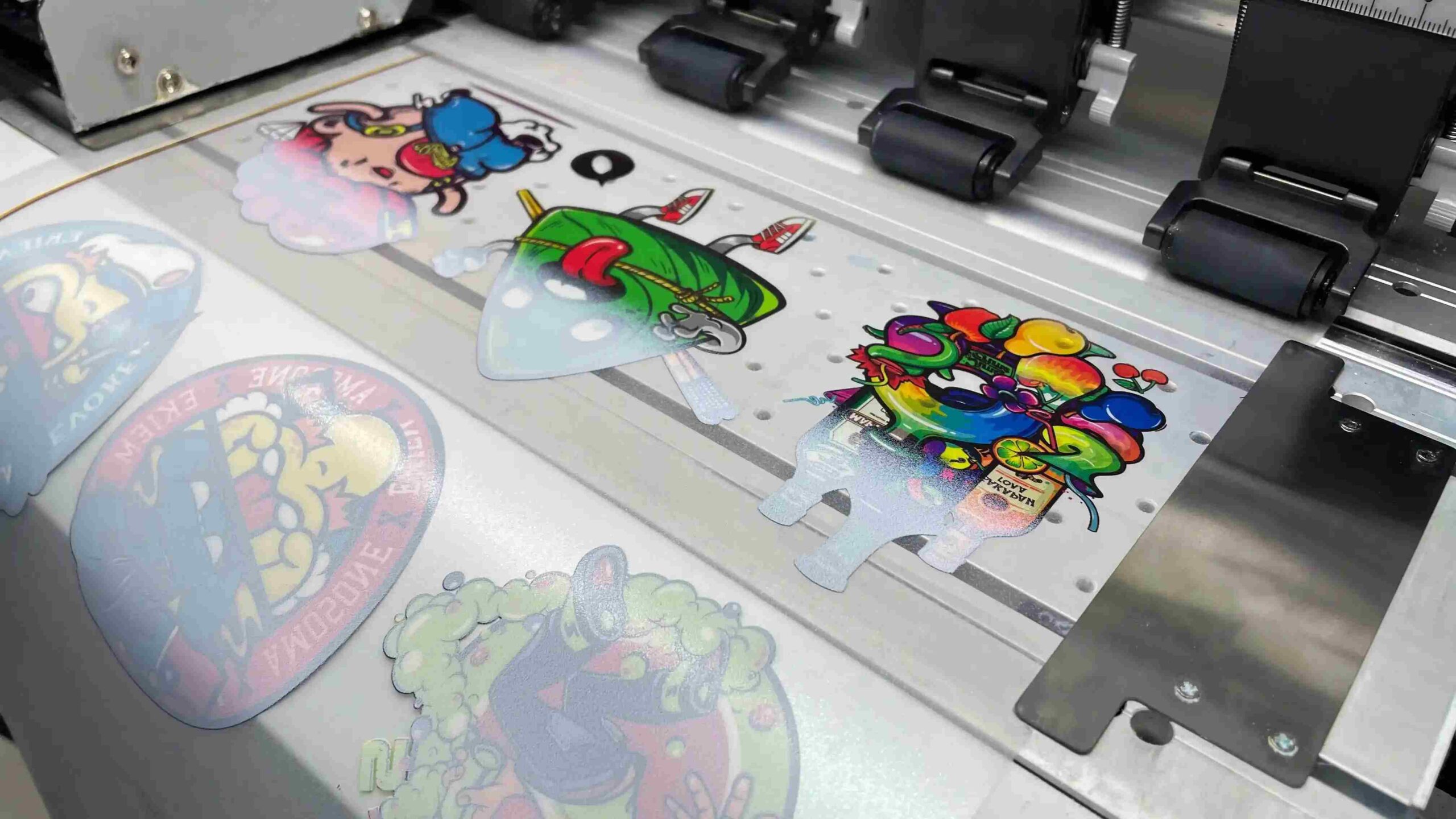
This density proves especially valuable on dark garments. Tests comparing coated films show noticeable improvements in saturation scores, with reds and blues appearing richer against black cotton.
Uniform distribution eliminates thin spots common in less capable surfaces. Ink spreads consistently rather than pooling, yielding smoother gradients and truer hues.
A packaging prototype series for consumer goods benefited from this. Graphic elements transferred with deeper contrast, enhancing shelf appeal without additional print passes.
The Role of Anti-Static Properties
Static interference disrupts DTF workflows in subtle ways.
Charged surfaces attract powder randomly, leading to over-application in some areas and insufficient coverage in others. This unevenness translates to weak adhesion after pressing.
Built-in anti-static agents dissipate charges as they form, keeping powder distribution controlled. Ink droplets land where intended rather than deflecting.
Dry workshop conditions highlight the difference. Traditional films often require humidifiers or manual grounding, while treated coatings perform steadily across varying humidity levels.
One large-format operation reduced powder waste significantly by minimizing excess adhesion, cutting both material costs and cleanup time.
Comparison with Traditional Coating Systems
Traditional multi-layer coatings involve distinct steps for release, absorption, and adhesion.
These approaches carry inherent drawbacks. Separate applications increase chances of inconsistency between layers, leading to peeling or variable performance across a roll.
Production complexity rises as well. Multiple coating passes extend manufacturing time and raise defect risks from alignment errors.
Single-layer integrated systems streamline the process. One application delivers release for clean separation, absorption for ink control, and adhesive activation for bonding.
Direct comparisons reveal advantages. Integrated coatings often show lower rejection rates in high-volume runs, with better tolerance for ink variations.
Cost considerations shift over time. Initial simplicity reduces processing expenses, while improved yield lowers per-unit waste.
A mid-sized printing facility tracked metrics before and after switching. Stability improved, color complaints dropped, and overall throughput rose without additional equipment.
Selection and Optimization Tips
Choosing suitable white ink absorbent coatings requires practical evaluation.
Start with compatibility testing. Run samples on actual printers with standard ink sets to observe absorption speed and release behavior.
Assess performance under production conditions. Simulate long runs to check for degradation in stability or density.
Storage matters. Keep rolls in controlled environments to preserve anti-static and absorption properties.
Maintenance complements coating choice. Regular white ink circulation prevents settling that stresses even good surfaces.
Decision frameworks help weigh options. Calculate waste reduction against material costs to reveal true economics.
Operations find that targeted testing quickly separates capable coatings from marginal ones.
Introducing Foshan Konaz Technology Co., Ltd.
Foshan Konaz Technology Co., Ltd. focuses on functional coatings for digital printing applications. The company maintains a 3000-square-meter production facility with more than 30 lines, supporting annual capacity over 1000 tons.
Its 3-in-1 white ink absorbent coating stands central to the range. This unified formulation combines release, high-absorption, and adhesive properties in one layer, serving PET film for DTF transfers worldwide.
Development emphasizes practical performance improvements, with customizable options addressing specific stability, density, and static challenges. Exports reach multiple markets alongside domestic digital printing material producers.

Conclusion
White ink absorbent coatings shape DTF print quality through better stability, richer colors, and controlled static behavior. Moving beyond traditional multi-layer approaches to integrated solutions brings measurable gains in consistency and efficiency.
Printing operations adopting advanced coatings position themselves for reliable output that meets rising demands for sharp, durable transfers across textiles and other substrates.
FAQs
How does white ink absorbent coating improve print stability in long DTF runs?
It rapidly draws ink into a stable structure, preventing settling or flow changes that cause banding over extended printing.
What contributes to greater color density with modern absorbent coatings?
Uniform high-volume ink holding creates opaque white bases that support vibrant overlays without substrate interference.
Why include anti-static properties in white ink absorbent coatings?
They prevent uneven powder adhesion and ink deflection, maintaining clean application especially in dry conditions.
How do integrated coatings compare to traditional multi-layer systems?
Single-layer designs reduce delamination risks and production complexity while delivering more consistent stability and release.
Which tests reveal coating performance before full adoption?
Sample runs checking absorption speed, color buildup, static behavior, and release under actual conditions provide clear indicators.