Introduction
Digital printing on PET film has transformed how patterns reach fabrics and other surfaces, particularly in direct-to-film processes. Yet many operations still grapple with issues that undermine final quality. Ink spreads unevenly across the surface, or colors fail to hold their vibrancy after transfer. These problems often trace back to one critical element: the white ink absorbent coating.
This coating plays a pivotal role when white ink absorbent coating matters for PET film printing. It determines how well white ink lays down as a base layer, preventing diffusion while ensuring subsequent colors appear sharp and saturated. Without a capable coating, white ink can pool or bleed, leading to distorted designs and higher rejection rates in production runs.
Consider a typical label production line where fine text and logos must remain crisp on varied substrates. Weak absorption causes the white underbase to shift, dulling overlays and forcing reprints. Strong coatings, by contrast, lock ink in place from the moment droplets hit the film. They create a matte white surface that accepts heavy white loads without overflow, setting the stage for reliable transfers in advertising materials, packaging graphics, and custom apparel.
Common Challenges in PET Film Printing
PET film offers excellent stability and heat resistance, qualities that make it ideal for heat transfer applications. Still, printers frequently encounter difficulties tied directly to ink behavior on the surface.
White ink, thicker and pigment-heavy compared to CMYK, tends to dominate these issues. When the underlying coating lacks sufficient holding capacity, excess ink migrates outward, creating halos around edges or muddy zones in solid areas. This diffusion becomes especially noticeable in high-resolution work, where precise boundaries separate colors.
Uneven coloring presents another widespread complaint. Operators notice patchy opacity in the white layer, allowing substrate tones to show through after transfer. In one packaging prototype run, inconsistent absorption led to visible streaks across large graphic blocks, rendering entire batches unusable for client approval.
Static buildup complicates matters further. Poorly formulated coatings attract dust or cause ink droplets to repel one another, resulting in gaps or clustering. Humidity fluctuations exacerbate these effects; moist environments slow drying, while dry conditions encourage cracking during curing.
These challenges carry real costs. Rejects climb, material waste grows, and deadlines slip as teams troubleshoot mid-run. Understanding root causes—primarily inadequate ink reception and release properties—points toward targeted solutions in coating selection.
How White Ink Absorbent Coating Works
Modern white ink absorbent coatings transform clear PET film into a functional printing medium. Applied as a single integrated layer, they combine multiple roles that once required separate applications.
The structure begins with a release component that allows clean separation after printing. Above it sits the absorbent matrix, typically microporous to draw ink rapidly inward. Finally, a hot-melt adhesive base activates under heat, bonding the design firmly to the target material.
When white ink hits this surface, capillary action pulls pigments into the pores almost instantly. This quick uptake prevents surface pooling, keeping droplets confined and maintaining edge definition. Colored inks layered on top benefit from the solid white foundation, achieving higher density without bleeding through.
Advanced formulations also incorporate anti-static agents, reducing particle attraction during printing. The result appears as a consistent matte white finish on the film, ready for heavy ink loads yet resistant to overflow even at 100% white coverage.
In practice, this mechanism shines during dense graphic work. A promotional banner job involving bold logos once suffered repeated smudging with conventional films. Switching to an integrated coating eliminated runoff, delivering clean sheets straight from the printer.
Key Benefits: Solving Diffusion and Uneven Coloring
Effective white ink absorbent coatings address the core pain points of PET film printing head-on. Their primary advantage lies in diffusion control.
By anchoring white ink securely, these coatings stop lateral spread that blurs fine details. Tests on intricate label designs show edge sharpness improving dramatically, with no visible halos even under magnification. This precision proves essential for barcode legibility and small text in packaging applications.
Even coloring follows naturally from uniform absorption. The porous layer distributes ink volume consistently across the sheet, eliminating thin spots that let substrate colors bleed through. Advertising prints gain true opacity, ensuring brand hues remain faithful regardless of fabric tone beneath.
Additional gains appear in production efficiency. Faster ink setting reduces drying time between white and color passes, allowing higher throughput without quality trade-offs. Clean release properties minimize residue on the film, cutting cleanup efforts and extending equipment life.
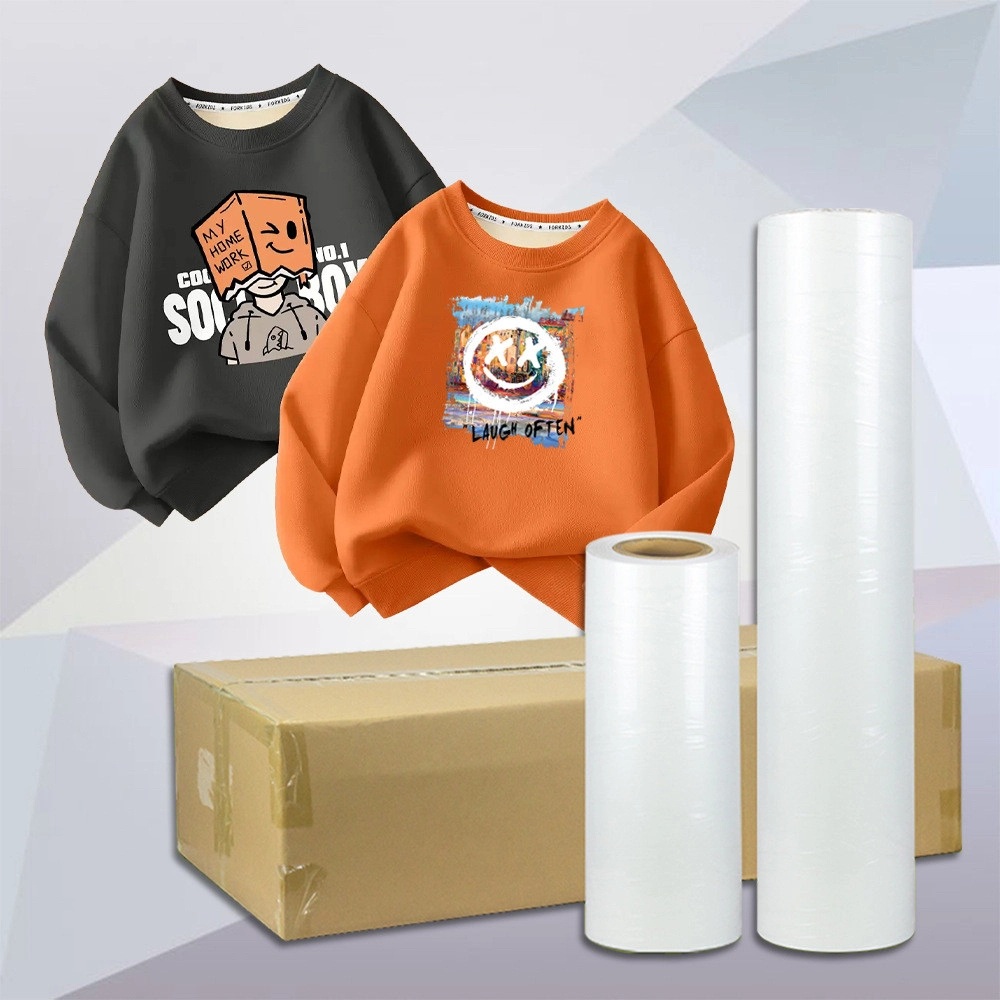

Durability after transfer also improves. Properly absorbed ink bonds more strongly with adhesive powder, resisting wash cycles and abrasion better than loosely held layers. Outdoor signage applications particularly benefit, maintaining vibrancy through weather exposure.
Applications and Real-World Examples
White ink absorbent coatings find broad use across industries relying on PET film transfers.
In label production, they enable sharp, durable graphics on bottles, containers, and consumer goods. One cosmetics manufacturer shifted to coated films for product tags, achieving finer text reproduction that elevated shelf presence while reducing returns due to illegible batch codes.
Advertising materials demand bold, saturated visuals. Large-format banners and point-of-sale displays transfer cleanly onto varied surfaces, from vinyl to textiles. A retail campaign featuring vibrant promotional graphics avoided color shifts that plagued earlier attempts, delivering consistent impact across multiple store locations.
Packaging patterns represent another strong fit. Food-safe transfers for flexible pouches or decorative boxes require precise registration and wash resistance. Coated films support intricate multicolored designs that adhere reliably, enhancing brand distinction without compromising barrier properties.
Beyond these, custom textile work benefits immensely. Apparel decorators produce detailed motifs on cotton, polyester, and blends, with white bases that flex without cracking. Event merchandise runs finish faster and with fewer defects, meeting tight turnaround demands.
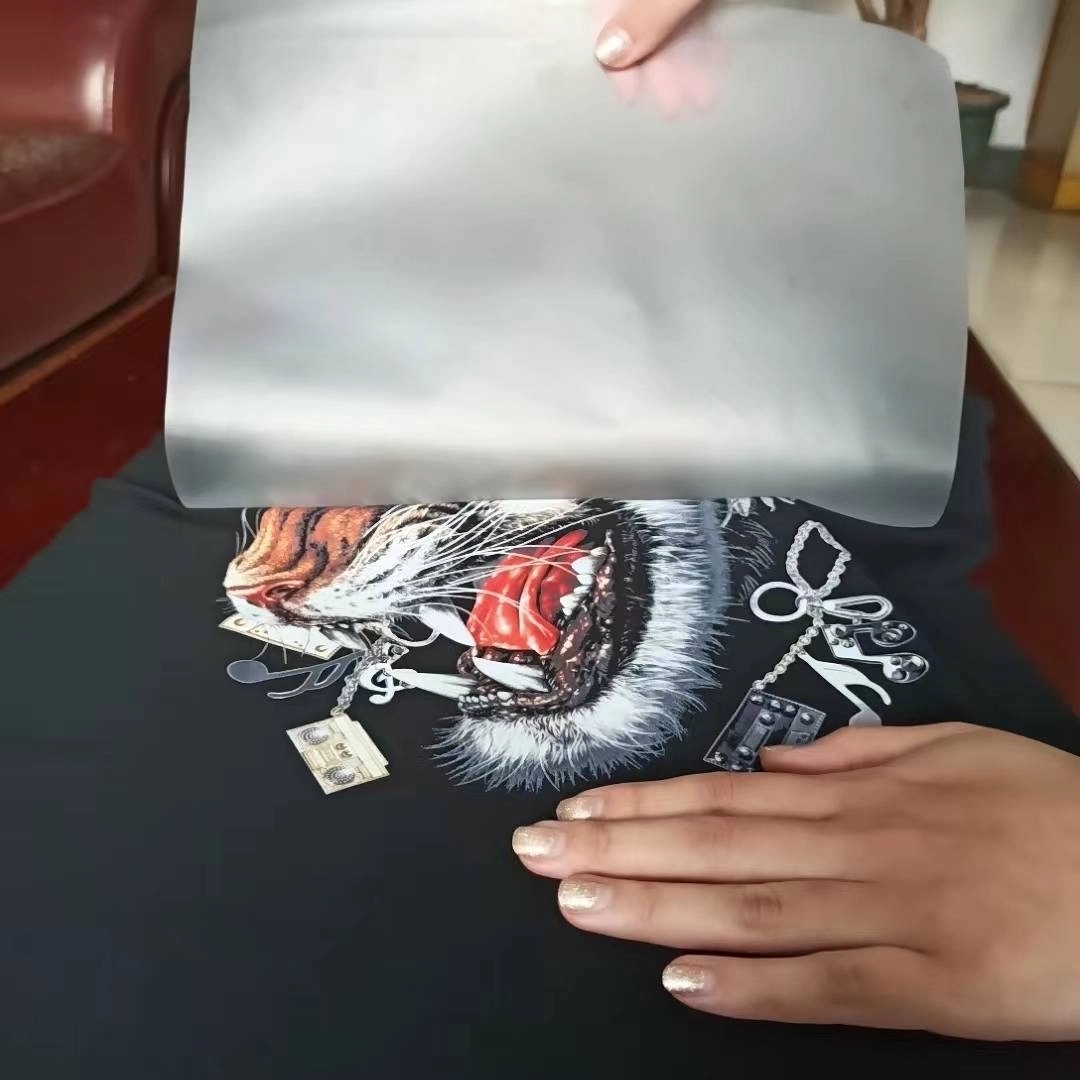

Choosing and Applying the Right Coating
Selecting an appropriate white ink absorbent coating involves several practical considerations.
Compatibility tops the list. Coatings must pair well with specific ink sets and printer configurations to avoid separation or poor flow. Sample testing on actual equipment reveals performance under real conditions.
Absorption capacity matters for heavy white usage. Formulations handling high ink volumes prevent overload in solid fills, while maintaining quick uptake for speed.
Release characteristics influence transfer success. Clean peel without residue preserves pattern integrity, especially important for delicate substrates.
Application method also factors in. Roll-to-roll operations favor coatings that maintain flatness and resist curling under heat. Sheet-fed setups benefit from anti-static properties that ease handling.
Prevention starts with storage. Keeping films in controlled environments avoids moisture uptake that impairs absorption. Regular printer maintenance—circulation for white ink, nozzle checks—complements coating performance.
Decision-making becomes straightforward with these criteria. Operations weighing cost against waste reduction often find premium coatings pay back quickly through lower rejects and higher output quality.
Introducing Foshan Konaz Technology Co., Ltd.
Foshan Konaz Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in advanced functional coatings for digital printing and industrial applications. The company operates a modern 3000-square-meter facility equipped with over 30 production lines, achieving annual output exceeding 1000 tons.
Central to its lineup stands the 3-in-1 white ink absorbent coating for PET transfer films. This single-layer solution integrates release, absorption, and adhesive functions, simplifying manufacturing while delivering high color density and stable performance. Products serve digital printing material producers worldwide, alongside sectors requiring heat-resistant protection.
Innovation drives ongoing development, with customizable formulations addressing diverse production needs. International exports have built recognition for reliability and technical support.
Conclusion
White ink absorbent coatings fundamentally shape outcomes in PET film printing. They resolve persistent challenges around diffusion and unevenness, enabling sharper details, richer colors, and more efficient workflows across labels, advertising, and packaging.
Operations adopting capable coatings gain predictable results that reduce waste and elevate finished quality. The shift represents not merely a material choice, but a foundation for consistent excellence in digital transfer processes.
FAQs
What causes ink diffusion on PET film during printing?
Weak absorption allows white ink to spread laterally, often due to overloaded or incompatible coatings that cannot contain heavy pigment loads quickly enough.
How does a strong white ink absorbent coating improve color evenness?
It distributes ink uniformly across the surface, creating a solid opaque base that prevents thin spots and ensures consistent overlay performance.
Why do some coatings lead to residue after transfer?
Poor release properties leave adhesive or ink traces on the film, whereas integrated formulations separate cleanly without compromising pattern integrity.
Which applications benefit most from advanced absorbent coatings?
Label production, advertising graphics, and packaging patterns gain sharp details and durable transfers, especially on varied substrates requiring high opacity.
How can printers test coating suitability before full runs?
Small-scale trials with actual inks and designs reveal absorption speed, edge definition, and release behavior under production conditions.